STARR Procedure - Single Stapler (Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection) for Rectal Prolapse
Hellow guys, Welcome to my website, and you are watching STARR Procedure - Single Stapler (Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection) for Rectal Prolapse. and this vIdeo is uploaded by Dr. R. K. Mishra at 2024-05-25T03:24:11-07:00. We are pramote this video only for entertainment and educational perpose only. So, I hop you like our website.
Info About This Video
| Name |
STARR Procedure - Single Stapler (Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection) for Rectal Prolapse |
| Video Uploader |
Video From Dr. R. K. Mishra |
| Upload Date |
This Video Uploaded At 25-05-2024 10:24:11 |
| Video Discription |
STARR Procedure: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
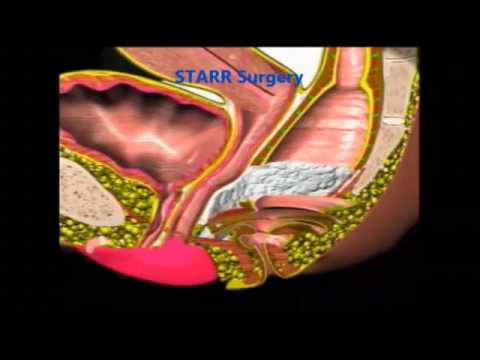
The STARR (Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection) procedure is a minimally invasive surgical technique designed to treat obstructed defecation syndrome (ODS), a condition often associated with rectal prolapse, rectocele, and intussusception. Introduced in the early 2000s, the STARR procedure has gained prominence for its efficacy in alleviating symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with refractory ODS.
Indications
The primary indication for the STARR procedure is obstructed defecation syndrome (ODS) that does not respond to conservative treatments such as dietary modifications, pelvic floor exercises, or pharmacotherapy. Patients with the following conditions may be considered for the STARR procedure:
Rectocele: A bulging of the rectum into the vagina.
Rectal intussusception: The telescoping of one part of the rectum into another.
Rectal prolapse: A condition where the rectum protrudes through the anus.
Preoperative Assessment
Before undergoing the STARR procedure, a thorough preoperative assessment is essential. This includes:
Clinical Evaluation: A detailed history and physical examination to assess the severity and impact of symptoms.
Imaging Studies: Defecography, MRI, or endoanal ultrasound to evaluate the anatomical abnormalities.
Manometry: Anorectal manometry to measure the pressures in the rectum and anal sphincter.
Colonoscopic Examination: To rule out other colonic pathologies.
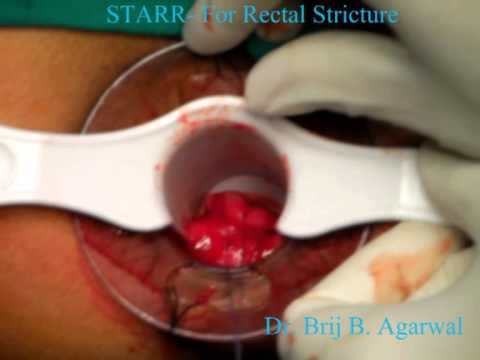
Surgical Technique
The STARR procedure involves the following key steps:
Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under general or regional anesthesia.
Patient Positioning: The patient is placed in the lithotomy position.
Insertion of Stapler: A specially designed circular stapler is inserted transanally.
Tissue Excision: The stapler is used to resect the redundant rectal tissue causing the obstruction.
Anastomosis: The stapler creates an anastomosis, joining the remaining rectal tissue ends.
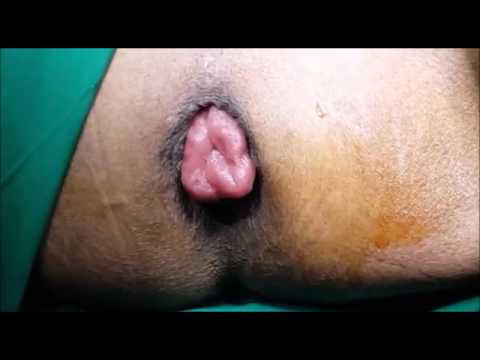
Hemostasis: Ensuring no bleeding and verifying the integrity of the anastomosis.
The entire procedure typically takes about 60-90 minutes.
Postoperative Care
After the STARR procedure, patients require close monitoring and appropriate postoperative care, which includes:
Pain Management: Administration of analgesics to manage pain.
Dietary Recommendations: A gradual reintroduction of diet starting with liquids and progressing to solid foods.
Laxatives: Mild laxatives may be prescribed to ensure smooth bowel movements.
Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments to monitor recovery and address any complications.
Complications
As with any surgical procedure, the STARR procedure carries potential risks and complications, including:
Bleeding
Infection
Anastomotic leak
Fecal incontinence
Urinary retention
However, these complications are relatively rare, and the overall success rate of the procedure is high.
Outcomes and Efficacy
Studies have shown that the STARR procedure effectively alleviates symptoms of obstructed defecation syndrome. Patients report significant improvements in bowel function, reduction in the need for manual evacuation, and overall enhancement in the quality of life. Long-term follow-up studies have also indicated sustained benefits with minimal recurrence of symptoms.
Conclusion
The STARR procedure represents a significant advancement in the surgical management of obstructed defecation syndrome. Its minimally invasive nature, coupled with high efficacy and low complication rates, makes it a valuable option for patients suffering from this debilitating condition. As with any surgical intervention, a thorough preoperative assessment and meticulous surgical technique are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.
For surgeons and healthcare providers, staying updated with the latest advancements and techniques in procedures like STARR is essential to provide the best care for patients.
Contact us
World Laparoscopy Hospital
Cyber City, Gurugram
NCR Delhi, India
World Laparoscopy Training Institute
Bld.No: 27, DHCC, Dubai, UAE
World Laparoscopy Training Institute
5401 S Kirkman Rd Suite 340
Orlando, FL 32819, USA |
| Category |
Education |
| Tags |
STARR procedure | obstructed defecation syndrome | ODS | rectocele | rectal intussusception | rectal prolapse | minimally invasive surgery | transanal surgery | stapled transanal rectal resection | colorectal surgery | anorectal manometry | defecography | MRI | endoanal ultrasound | circular stapler | anastomosis | postoperative care | surgical complications | bowel function | colorectal treatment |
More Videos

.png)